The aorta artery is the main blood vessel of the body. It originates in the heart and extends to the pelvis through the thorax and abdomen from top to bottom and slightly to the left. Its main function is to channel all the oxygenated blood that pumps the heart to distribute it throughout the body.
What is an aneurysm?
An aneurysm is a pathological dilatation in a segment of a blood vessel that is usually caused by weakness of the wall of the same, being unable to support the tension exerted on it by the blood that leaves the heart. This weakness is usually related to atherosclerosis, the degenerative process of the arteries and all the risk factors that accelerate it: hypertension, cholesterol, smoking, obesity, chronic bronchitis … etc.
What symptoms does it produce?
The aneurysm of the aortic artery is known as the “silent killer”, basically because it does not produce any symptoms until it breaks. This pathology develops very slowly and is usually identified incidentally in radiological tests that are requested for other reasons, such as an abdominal ultrasound for a prostate study.
Is it dangerous to have an aneurysm?
The rupture of an aortic aneurysm is a deadly event. It is estimated that about 80% of patients suffering from it end up dying, most of them without even being able to reach a hospital. From certain diameters (between 5 and 6cm) and depending on their location, the risk of breakage increases exponentially, which is why it is very important to identify them and control their growth over time.
Can I have an aneurysm?
Aneurysms usually develop in patients older than 60 years with cardiovascular risk factors. The presence of arterial hypertension, smoking and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis / emphysema) are particularly relevant. Although they are quite more frequent in men, women have a greater risk of rupture and a worse prognosis in the treatment..
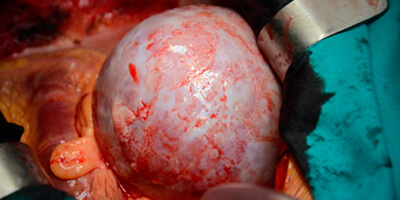
Aortic aneurysms are characterized by a weak and diseased aorta wall in the largest blood vessel in your body. This can become a health problem that can be fatal if the aneurysm ruptures, causing a massive internal hemorrhage of your abdomen.
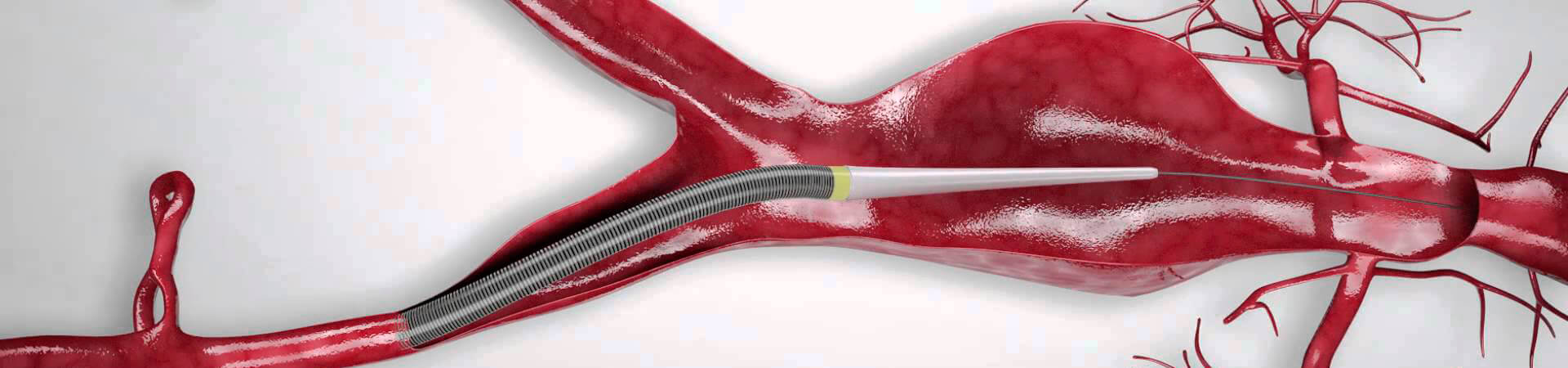
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a treatment method for aortic aneurysms, less invasive and with a lower risk of complications than traditional open surgery. A coated endoprosthesis is used to reinforce the aorta wall inside and depressurises the aneurysm to prevent rupture, thus stopping its growth and beginning a phase of progressive reduction of its size.
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is an interventional surgical procedure performed inside the aortic artery accessed through a kind of hollow thin tube called a catheter. Unlike open surgery, which involves a large incision along the abdomen and a complex postoperative period, endovascular surgery requires only two punctures or mini-incisions in the groin area, and in most cases does not require any suture. The procedure usually lasts 1 to 2 hours, and can be performed under local or regional anesthesia, that means much shorter reparation period than the aneurysm repair by open surgery that always requires general anesthesia and an estimated duration of 2 to 4 hours.
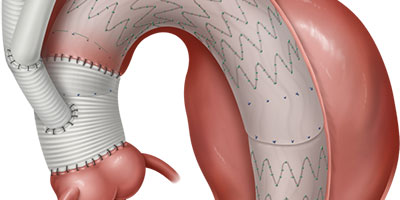
You can expect to return to your normal life after the implantation of an endovascular stent for the treatment of your AAA, and there is no complicated postoperative period when compared to open surgery, at 48-72 hours you can go back to your life usual, but that does not necessarily mean that you should return to old habits such as smoking.
EVAR therapy with endoprostheses for the treatment of aneurysms has already demonstrated in multiple international studies and clinical trials its effectiveness in the prevention of rupture of AAA and has been established as the therapy of choice in the main centers of global cardiovascular reference.
Endovascular therapy, like surgery, requires subsequent monitoring and follow-up, so you will have to undergo a examination at least once a year, during your entire life with your Angiologist or Vascular Surgeon, that, through an abdominal ultrasound or a scanner if it’s neccessary, will perform a control of the size of your aneurysm after the stent is implanted. Thanks to advances in ultrasound, the use of scanners has been reduced to a minimum and therefore the patient’s radiation risk.

The indication to use an endovascular stent to treat your aneurysm depends on several factors, especially anatomical, that is the shape, location and size of the aneurysm and the general condition of the patient.
The doctor will perform a medical examination and several tests to help decide if the use of EVAR with an endovascular stent is right for you.
The endovascular stent prevents rupture of the aneurysm, but you should be aware of your disease and make the necessary changes in your lifestyle to avoid complications.