Each year, 15 million people worldwide suffer a stroke, also known as stroke or cerebral infarction. This event has a high mortality, up to 40% of patients who suffer from it die, and more than 30% of those who survive have some type of disability. Carotid artery disease is estimated to be the cause of ischemic stroke in up to one third of cases.
This vascular disease is caused by the progressive development of atheromatous plaques that deteriorate the lining of the arteries, in a process known as atherosclerosis. As the atheroma plaques develop, they thicken the wall of the artery decreasing the light of the vessel more and more, until causing a stenosis that ends up limiting the blood flow to the tissues and vital organs.
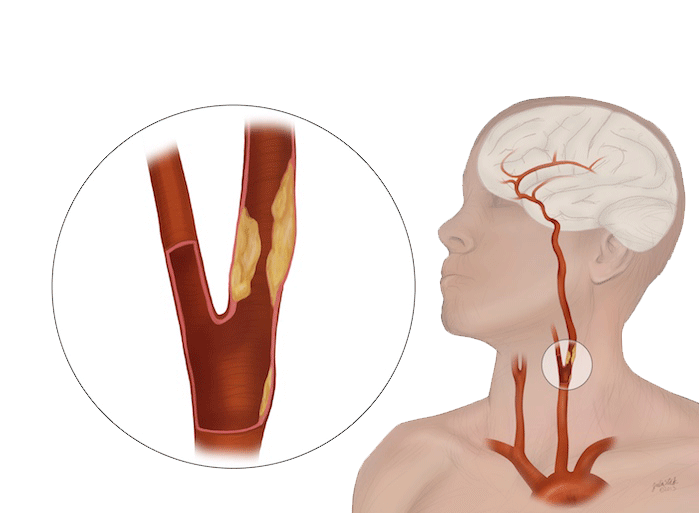
When the atheroma plaques accumulate in the carotid arteries, they can detach fragments of thrombus or cholesterol that travel and obstruct cerebral arteries, causing an ischemic cerebrovascular accident.
If the stenosis in the carotid artery is detected early and is greater than 80% of the lumen of the vessel, repair is indicated in most cases, although the patient has not yet presented any symptoms. If the patient has already presented some symptom, the presence of a stenosis above 50% may already be indicative of revascularization treatment.
It is very important that high-risk patients (hypertensive, high cholesterol, diabetics …) undergo ultrasound screening programs to prevent a possible stroke.
On the other hand, patients who present any of these symptoms should undergo an ultrasound screening test for carotid artery disease:
- Weakness, numbness, tingling, or paralysis of the arm, leg, or face on one side of your body
- Sudden loss of memory
- Loss of vision or blurred vision in one eye
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Speech or language problems
Stenosis in the carotid artery can be addressed basically in three different ways:
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA): A traditional technique that involves the surgical exposure of any carotid arterial sector through a longitudinal incision along the entire lateral aspect of the neck.
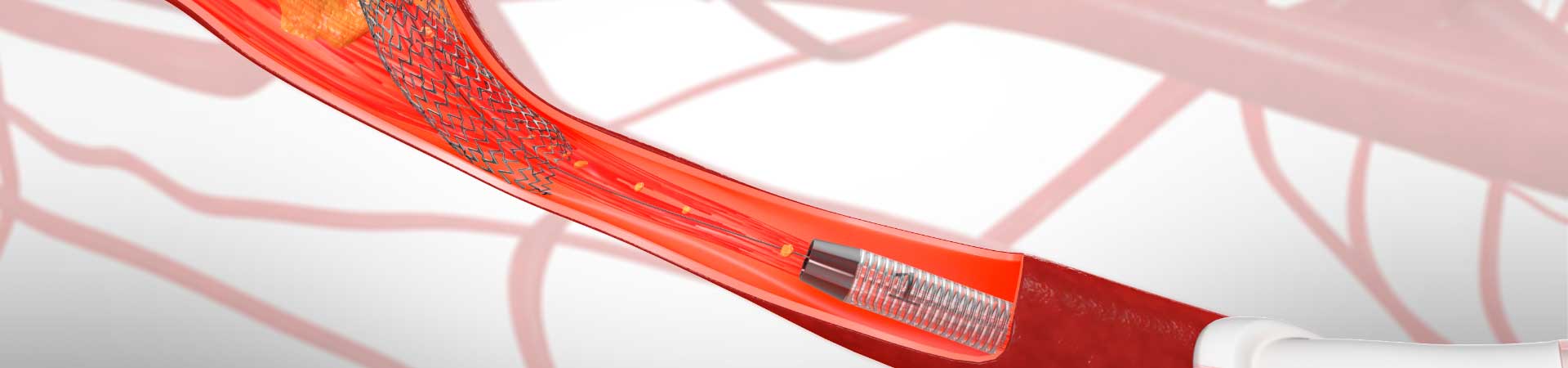
- Transfemoral carotid stenting: Technique less invasive than CEA, which can be performed under local anesthesia. It is performed by puncture in the femoral artery and through a catheter system the carotid artery dilates from within and a Stent is implanted to keep it open.
- TRANSCERVICAL carotid stenting or HRCT technique: It is the state-of-the-art technique for the treatment of carotid stenosis. Similar to transfemoral stenting with the difference that we access the carotid artery directly from the neck.
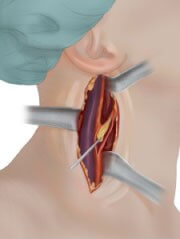
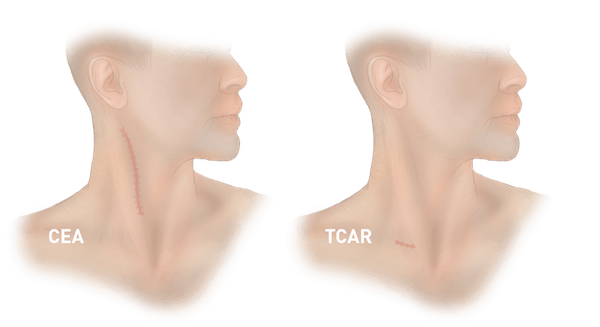
Transcervical revascularization of the transcarotid artery (TCAR) is an alternative, clinically proven, less invasive than the usual open surgery: carotid endarterectomy (CEA), and much safer than transfemoral stenting.
The TCAR procedure is performed through a small incision just above the clavicle. The surgeon will place a tube directly into the carotid artery and connect it to a system that will temporarily direct blood flow away from the brain, to protect it from hazardous waste that may be released from the atheromatous plaque during the procedure. Blood will flow through the system and any material will be captured in a filter outside the body. The blood from the filter will be returned through a second tube connected by puncture to a vein in the upper part of the thigh. This system of cerebral protection is the key to the success of the TCAR and what makes the difference with the rest of available treatments.
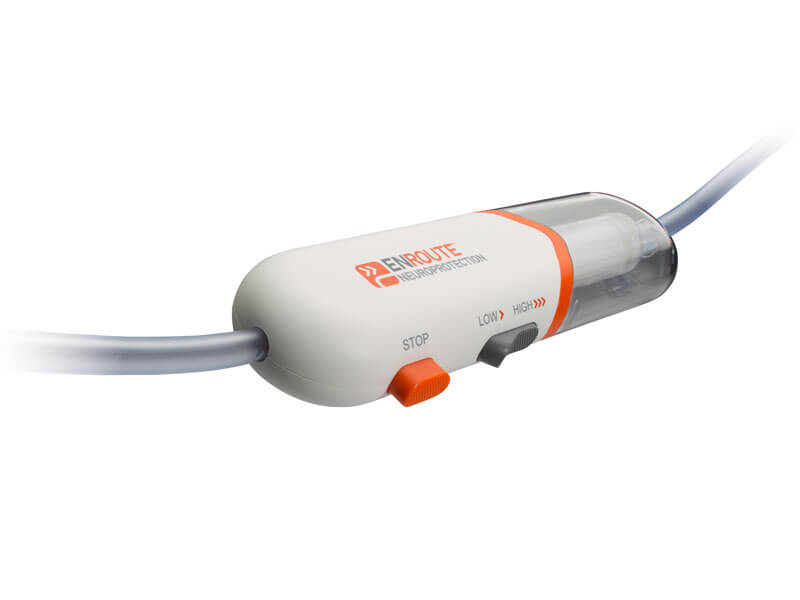
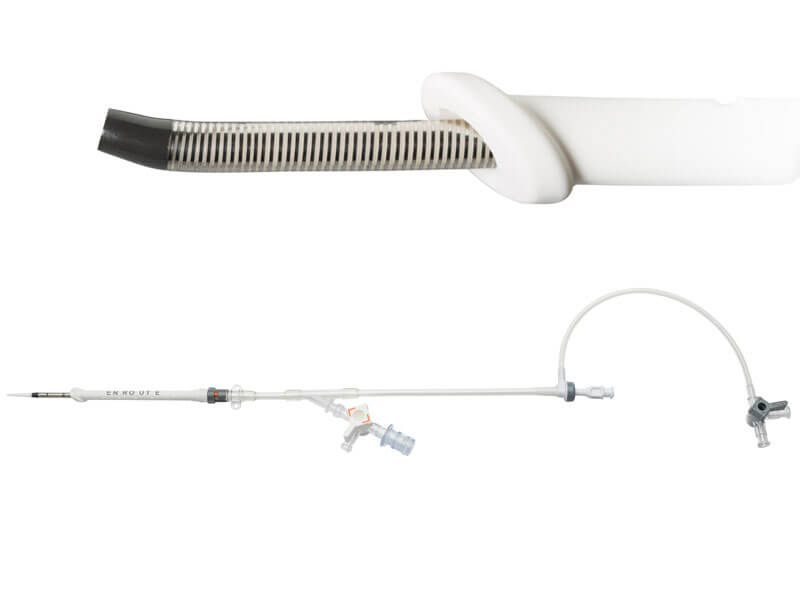

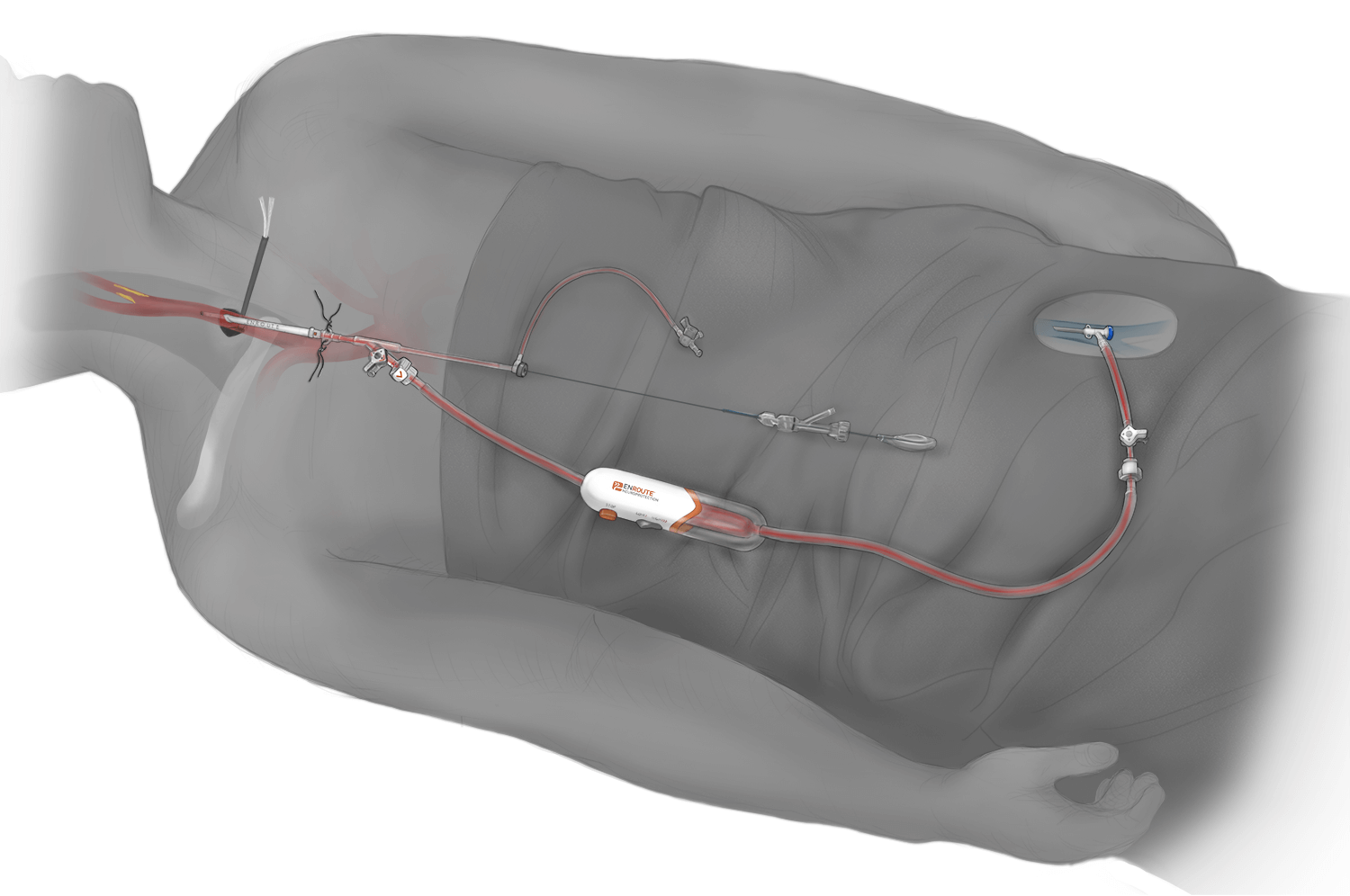
A carotid stent will be implanted to stabilize the plaque and prevent future strokes. After the Stent is successfully placed, the inversion of the flow is disconnected and the blood flow resumes in its normal direction.
The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia, with the patient awake at all times. This allows the patient’s brain function to be evaluated and monitored continuously.
In all procedures for the treatment of carotid stenosis (endarterectomy, transcervical stenting or TCAR) there is always a certain risk that stroke may occur during the procedure, due to the manipulation of the diseased artery.
Transcervical revascularization of the carotid artery (TCAR) has the lowest rate of cerebrovascular accidents related to the procedure (1.4%) according to the clinical studies available to date, compared to the 2.3% presented by classic endarterectomy or the 4.1% presenting transfemoral stenting.
In IVEI, all our specialists are adequately trained in all the techniques of carotid revascularization, being also experts in the TCAR procedure, the safest and most innovative treatment technique for this pathology. We have some of the surgeons with the most experience in this field at a national and international level, such as Dr. Rubén Rodríguez Carvajal, director of IVEI, who participated in the development of the TCAR technique in its beginnings and has extensive experience in its management , being also a principal investigator in the Roadster 2 study, a worldwide clinical trial in which only carefully selected centers participate because of their high training, with our IVEI team being the only participants in this trial throughout the national territory.